Glaucoma is a disease that damages the optic nerve progressively. If left untreated, this damage can cause vision loss. The optic nerve at the back of the eye becomes compromised due to increased pressure or other factors that affect the health of the nerve fibres.
Although there are different types of glaucoma, most forms do not exhibit noticeable symptoms in the early stages. This is why regular eye examinations are critical, especially for high-risk individuals. Early detection through testing is crucial in preventing irreversible vision loss.
What Is Glaucoma?
Glaucoma is an eye disease that happens due to very high pressure within the eye. Extra fluid buildup inside the eye increases the pressure in your eye, damaging the optic nerve, which supplies visual information from your eyes to the brain. If it’s detected early, you may be able to prevent additional vision loss. Early detection is key as glaucoma is the 2nd leading cause of blindness globally.
What Are the Types of Glaucoma?
There are two broad classifications of Glaucoma – Primary Glaucoma and Secondary Glaucoma.
Let’s embark on a detailed exploration of types of glaucoma and understand their individual characteristics, such as signs, symptoms, risk factors, remedies for glaucoma, and treatments.
Primary Glaucomas
Certain types of Glaucoma are caused by underlying medical conditions. However, sometimes, the doctor cannot detect a cause or condition for Glaucoma. In such cases, it’s known as Primary Glaucoma.
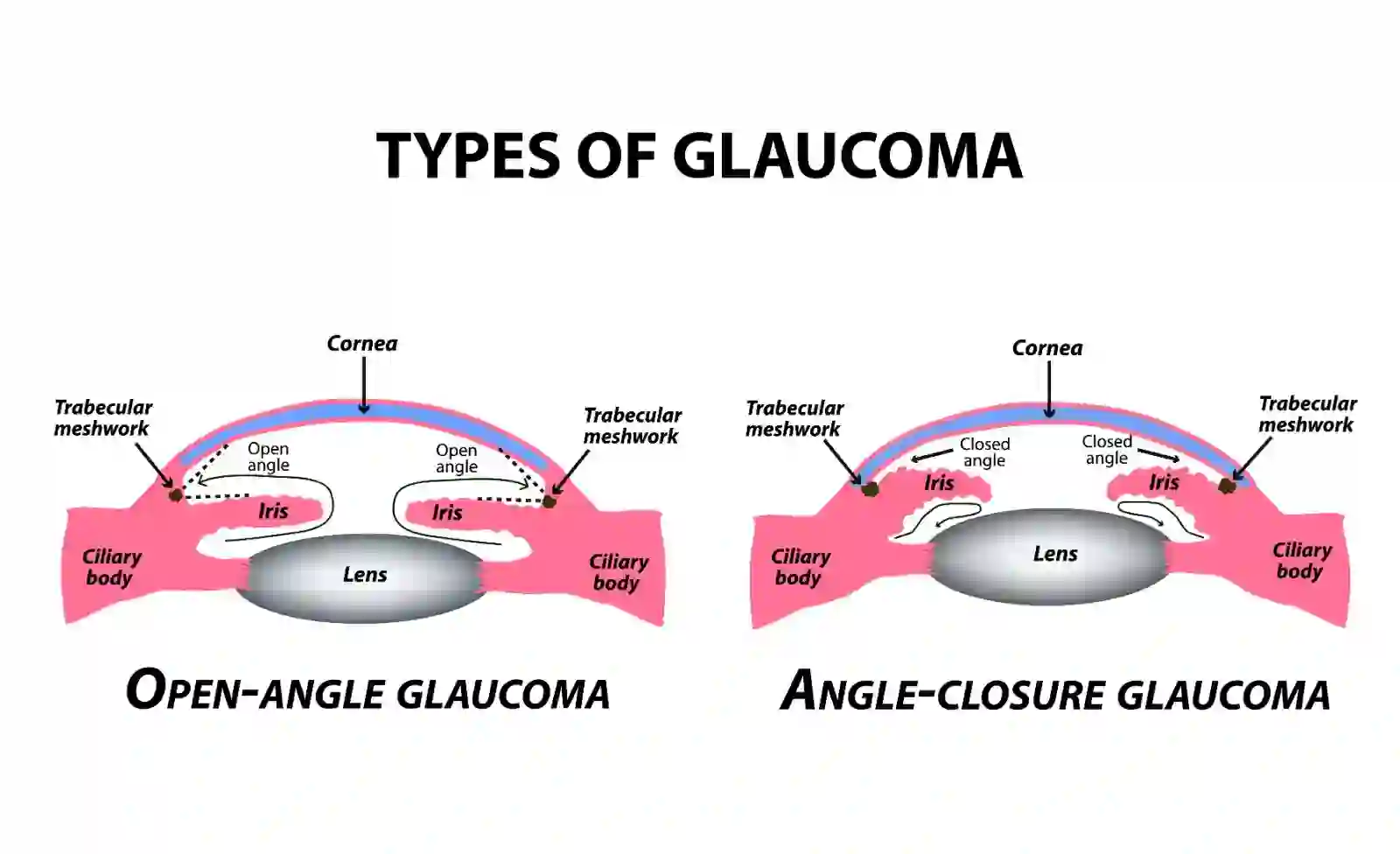
Open-Angle Glaucoma
Treatment Options: Medications, laser therapy, surgery
Primary open angle glaucoma is the most common form of the condition. Individuals may not notice symptoms until vision loss begins, making early detection difficult. Although the exact cause is not fully known, it is thought to result from pressure building within the eye due to fluid drainage issues. Over time, this pressure damages the optic nerve, potentially leading to vision loss. Individuals with certain health conditions are more likely to develop primary open angle glaucoma.
Normal-Tension Glaucoma
Treatment Options: Medications, laser therapy, surgery
Normal-tension glaucoma is a type of glaucoma that occurs even when eye pressure is within the normal range.
Certain factors can put you at a higher risk, such as:
- Family history of normal tension glaucoma
- Heart conditions such as irregular heartbeat
- Low blood pressure
While the cause is still unclear, lowering eye pressure has been shown to help slow its progression and prevent further vision loss.
Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma
Treatment Options: Medications, laser therapy
Primary angle closure glaucoma, also known as narrow-angle or acute glaucoma, is a medical emergency.
Symptoms of angle-closure glaucoma may include:
- Intense Eye pain
- Headache
- Blurred vision
- Red eyes
- Glare & halos
This condition occurs when the iris blocks the drainage of fluid, leading to a rapid increase in eye pressure. If left unattended, it can lead to vision loss. Medical intervention, such as laser therapy and medications, is essential to reduce pressure and protect vision.
There is also a slower-developing version of acute angle closure glaucoma that may not have noticeable symptoms. It can be managed with medications, laser treatments for glaucoma, or surgery.
Congenital Glaucoma
Treatment Options: Medications, surgery
Primary congenital glaucoma occurs in infants who are born with abnormal eye development, leading to fluid drainage issues. If your child is born with glaucoma, the signs are usually noticeable right away. Children with congenital glaucoma:
- Have cloudy eyes
- Are sensitive to light
- Have immensely teary eyes
- May have eyes that are larger than normal
Early surgery is generally effective in preventing permanent vision problems. Any glaucoma affecting infants or young children is called pediatric glaucoma.
Secondary Glaucoma
Glaucomas that occur due to an underlying medical condition are called secondary glaucomas.
Neovascular Glaucoma
Treatment Options: Medications, laser therapy, surgery
Neovascular glaucoma develops when abnormal blood vessels form and block fluid drainage in the eye. This condition is typically linked to other health issues. In the case of neovascular glaucoma, one may notice pain or redness in the eye and vision loss
Although this type of glaucoma is hard to treat, any treatment focuses on managing both the underlying conditions (such as diabetes or high blood pressure) and the glaucoma itself.
Pigmentary Glaucoma
Treatment Options: Medications, laser therapy, surgery
Pigmentary glaucoma is a type of glaucoma that occurs when the pigment from the iris flakes off and obstructs the eye’s drainage system. Symptoms may include blurry vision or seeing halos around lights. Treatments can reduce eye pressure, though there is no way to prevent the pigment from detaching.
Exfoliation Glaucoma
Treatment Options: Medications, laser therapy, surgery
Exfoliation glaucoma is a type of glaucoma that affects some people with exfoliation syndrome. It is a condition that causes excess material to deposit on parts of the eye, impeding fluid drainage.
The risk of developing this condition is higher if there’s a family history of exfoliation glaucoma.
This type of glaucoma can progress faster than primary open-angle glaucoma and often causes higher eye pressure. Therefore, anyone at a higher risk must get regular eye exams to protect their vision.
Uveitic Glaucoma
Treatment Options: Medications, surgery
Uveitic glaucoma can occur in people with uveitis, a condition that causes swelling and inflammation in the eye. Although experts aren’t sure about the correlation between Uveitis and Glaucoma, they think it is because uveitis can cause swelling and scar tissue in the centre of the eye. Inflammation and scar tissue can block fluid drainage, leading to elevated eye pressure, leading to uveitic glaucoma and vision loss.
Some steroid medicines that treat uveitis may also lead to uveitic glaucoma or make it worse because steroids are known to increase eye pressure as a side effect.
Other Causes
Glaucoma can also result from other health conditions or eye injuries. Wearing protective eyewear during certain activities can help reduce the risk of injury-related glaucoma.
Understanding the signs, symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options for each type of glaucoma is essential for proactive eye care. Regular eye check-ups aid in early detection and the implementation of effective management strategies. By staying informed about different types of glaucomas and treatments and taking preventive measures, individuals can work towards preserving their vision and minimising the impact of glaucoma on their eye health.
Combining comprehensive eye exams and advanced imaging techniques forms a great diagnostic strategy for glaucoma. This integrated approach enables healthcare professionals to detect glaucoma at various stages, facilitating early intervention and the implementation of effective management strategies.
FAQs
What are the different types of glaucoma?
There are several types of glaucoma – open-angle, angle-closure, normal-tension, congenital, and secondary glaucoma, each with varying causes and symptoms.
What is Grade 4 glaucoma?
Grade 4 glaucoma refers to an advanced stage of glaucoma where significant optic nerve damage has occurred, often resulting in severe vision loss or blindness.
Which glaucoma is more serious?
Primary angle closure glaucoma is typically considered more severe because it can cause a rapid increase in eye pressure and lead to blindness if not treated immediately.
Is glaucoma 100% curable?
Glaucoma is not 100% curable, but early detection and treatment can manage the condition and help prevent significant vision loss.
What is high-risk glaucoma?
High-risk glaucoma refers to cases where individuals have certain risk factors, such as a family history, diabetes, or elevated eye pressure, making them more likely to develop glaucoma.
What is the difference between primary glaucoma and secondary glaucoma?
Primary glaucoma occurs without any identifiable underlying cause, while secondary glaucoma results from another medical condition, such as an injury or eye disease.