|
Key Takeaways:
|
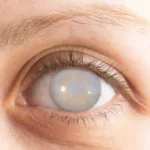
Posterior capsular opacification (PCO) is the clouding of the thin capsule behind the lens implant after cataract surgery. People often confuse it with a cataract “coming back” or refer to it as a posterior capsular cataract, which can be misleading.
This page explains what posterior capsular opacification (PCO) is, why it happens, the symptoms to watch for, and how doctors clear it safely with a quick YAG laser treatment.
What Is Posterior Capsular Opacification (PCO)?
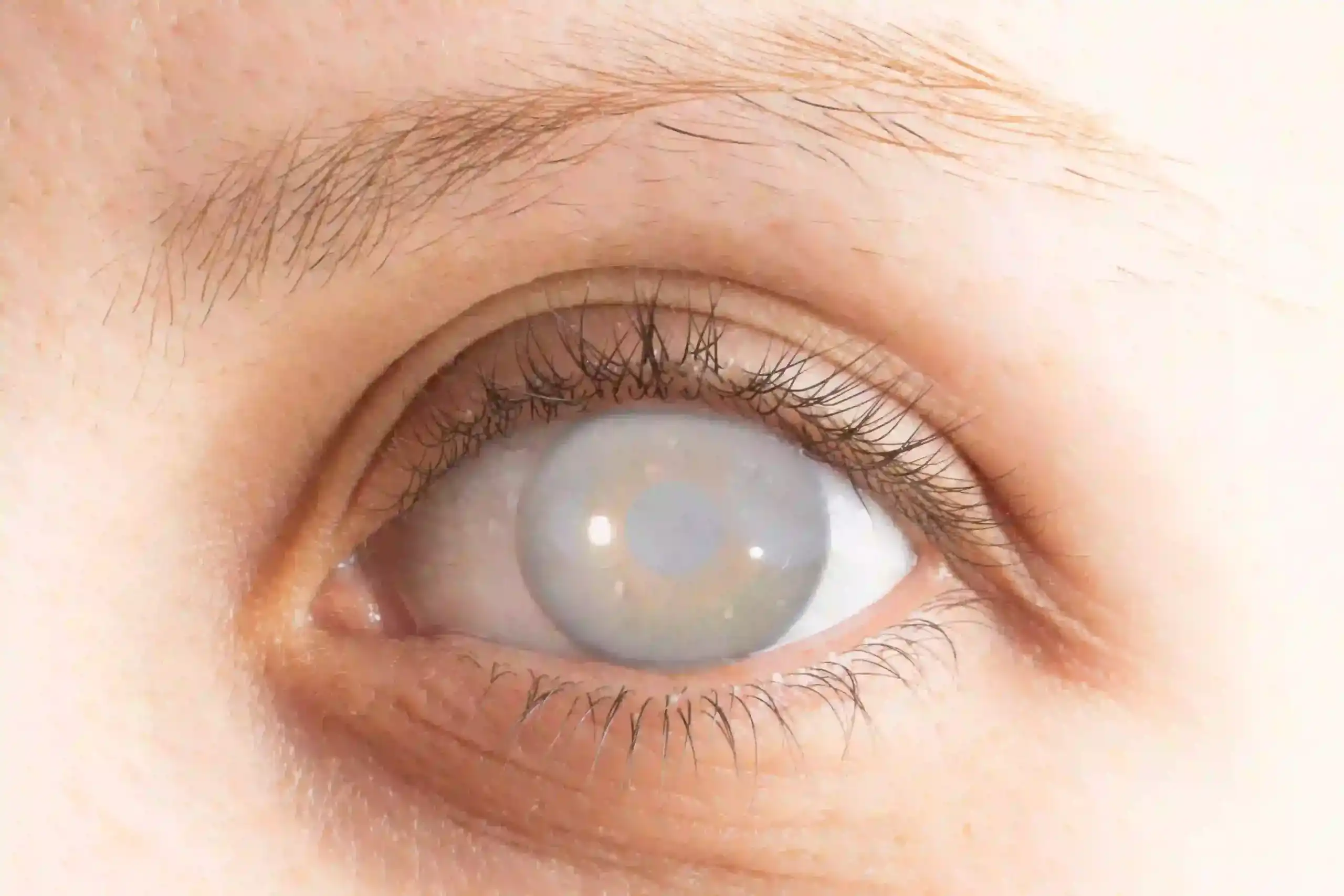
Posterior capsular opacification (PCO) is a common change that can happen after cataract surgery. People call it a “secondary cataract” because the vision becomes cloudy again, similar to looking through smudged glass, even though the original cataract was removed.
It isn’t the cataract growing back; instead, the thin back layer of the lens capsule (which holds the artificial lens in place) becomes cloudy over time. During surgery, the cloudy natural lens is taken out and a clear artificial lens (IOL) is placed inside the same capsule. The back part of this capsule stays in your eye to support the IOL.
Over time, residual LECs can proliferate and migrate onto this posterior capsule, causing fibrosis (a thin scar-like film) or Elschnig pearls (pearl-like cell clusters), which lead to glare, halos, and blurred vision.
Posterior Capsular Opacification (PCO) Causes
PCO occurs when the capsule behind the new lens becomes cloudy, which is why vision can seem blurry again after an initially clear post-surgery period.
A few things make this more likely:
- Cell growth after surgery: Residual lens epithelial cells continue to divide and migrate onto the back capsule, forming a thin, fibrous, or pearl-like layer.
- Post-op inflammation: Normal healing signals can encourage these cells to thicken the capsule surface.
- IOL material and design: Certain lens types help reduce cell migration; for example, many hydrophobic acrylic lenses are designed to lower the risk of PCO.
- Surgical technique: Careful cleaning of lens cells and a well-centred, properly sized capsulorhexis (the opening in the capsule) helps maintain a clearer capsule for a longer period.
Posterior Capsular Opacification (PCO) Symptoms
Posterior capsular opacification (PCO) symptoms can feel like the cataract has “come back,” because the vision issues are similar and usually build up slowly.
- Blurry vision: Gradual loss of clarity, like looking through a fogged window.
- Glare and halos: Lights look harsh or star-burst, and night driving becomes harder.
- Reduced contrast: Trouble seeing in dim rooms or against similar-coloured backgrounds.
- Monocular diplopia (double/ghost images in one eye): A faint second image that makes fine work tiring.
- Diminished visual sharpness: Fine detail becomes harder to see, which can affect reading and daily tasks
Types of Posterior Capsular Opacification (PCO)
Doctors describe Posterior Capsular Opacification (PCO) by the pattern of the cloudy layer on the back of the lens capsule.
- Fibrotic PCO: The capsule appears thickened or wrinkled, scattering light and softening clarity.
- Elschnig’s pearls: Tiny pearl-like clusters that scatter light and soften clarity
- Mixed PCO: A combination of fibrotic changes and pearls, more disturbing to vision.
Diagnosing Posterior Capsular Opacification (PCO)
Your eye doctor can confirm PCO with a quick clinic exam and simple tests.
- Slit-lamp exam: A microscope check to see the cloudy layer on the capsule.
- Vision/acuity test: Measures how much clarity has been lost.
- Dilated exam: Eye drops widen the pupil, allowing the doctor to see the capsule clearly and assess the density of the haze.
Treatment for Posterior Capsular Opacification (PCO)
The go-to treatment for PCO is YAG laser capsulotomy. It’s a quick, clinic-based procedure that doesn’t involve cuts or stitches. Most people feel little to no discomfort, and vision usually clears soon after.
YAG Laser Capsulotomy Procedure:
- Preparation: Your eye is dilated with drops, allowing the doctor to see the posterior capsule clearly.
- Laser application: The YAG laser makes a tiny opening in the center of the cloudy capsule, creating a clear path for light to reach the retina.
- Vision improvement: Many patients notice sharper vision within hours, with glare and halos easing as the eye settles.
- Back to routine: Recovery is minimal; you can return to normal activities the same day unless your doctor advises otherwise.
Risks and considerations
- Temporary rise in eye pressure
- Floaters (small moving spots)
- Retinal detachment (rare but serious, seek care fast if you see sudden flashes, a curtain over vision, or many new floaters)
Conclusion
Most cases of posterior capsular opacification are easy to diagnose and fix. If your vision becomes cloudy again after cataract surgery, a quick clinic procedure called YAG laser capsulotomy typically restores clarity. Risks are rare, recovery is fast, and most people notice sharper vision the same day. If your symptoms match, book an eye exam to confirm the cause and plan treatment.
FAQs
What does opacification mean?
The meaning of opacification is that a once-clear tissue becomes cloudy and scatters light, reducing vision.
What is PCO’s full form in ophthalmology?
The PCO full form in ophthalmology is posterior capsular opacification.
What treatment options are available for managing PCO and regaining clear vision?
The treatment options for PCO are led by YAG laser capsulotomy, which makes a small opening in the cloudy capsule to clear the visual axis.
Can Posterior Capsular Opacification be prevented?
Yes, Posterior Capsular Opacification can be reduced by modern IOL design and careful surgical steps, but it cannot be fully prevented in every eye.
Can Posterior Capsular Opacification go away?
No, Posterior Capsular Opacification does not clear on its own and usually needs YAG laser treatment.
Can posterior capsular opacification return?
Yes, posterior capsular opacification can rarely recur, though most patients remain clear after an adequate laser opening.
What are the symptoms of Posterior Capsular Opacification?
The symptoms of Posterior Capsular Opacification are gradual blur, glare or halos (especially at night), reduced contrast, and sometimes a faint ghost image in one eye.
How common is PCO?
The commonness of PCO is high; it is one of the most frequent causes of blurred vision months to years after cataract surgery.
How long after cataract surgery can posterior capsular opacification occur?
The timing of posterior capsular opacification can range from a few months to several years after surgery.
What are the common symptoms of PCO, and how can I recognize them?
The common symptoms of PCO are foggy vision, harsh headlights, and needing more light to read; recognizing them involves noticing these changes despite wearing new glasses.
Why does PCO occur after cataract surgery?
The reason PCO occurs after cataract surgery is that leftover lens epithelial cells grow on the posterior capsule and make it hazy.
What are the posterior capsular opacification types?
There are 3(three) different types of posterior capsular opacification: fibrotic PCO, Elschnig’s pearls, and mixed PCO.
What is posterior capsular opacification?
Posterior capsular opacification is a cloudy film that forms on the posterior capsule behind the lens implant after cataract surgery.
How is posterior capsular opacification treated?
Posterior capsular opacification is treated with a quick, clinic-based YAG laser capsulotomy that clears a path for light.
Can posterior capsular opacification be corrected?
Yes, posterior capsular opacification can be corrected, and most people regain clear vision after YAG laser capsulotomy.
How to prevent posterior capsular opacification?
The ways to prevent posterior capsular opacification include using modern IOLs, thorough cell cleanup, and proper capsule overlap, which lower the risk but do not make it zero.