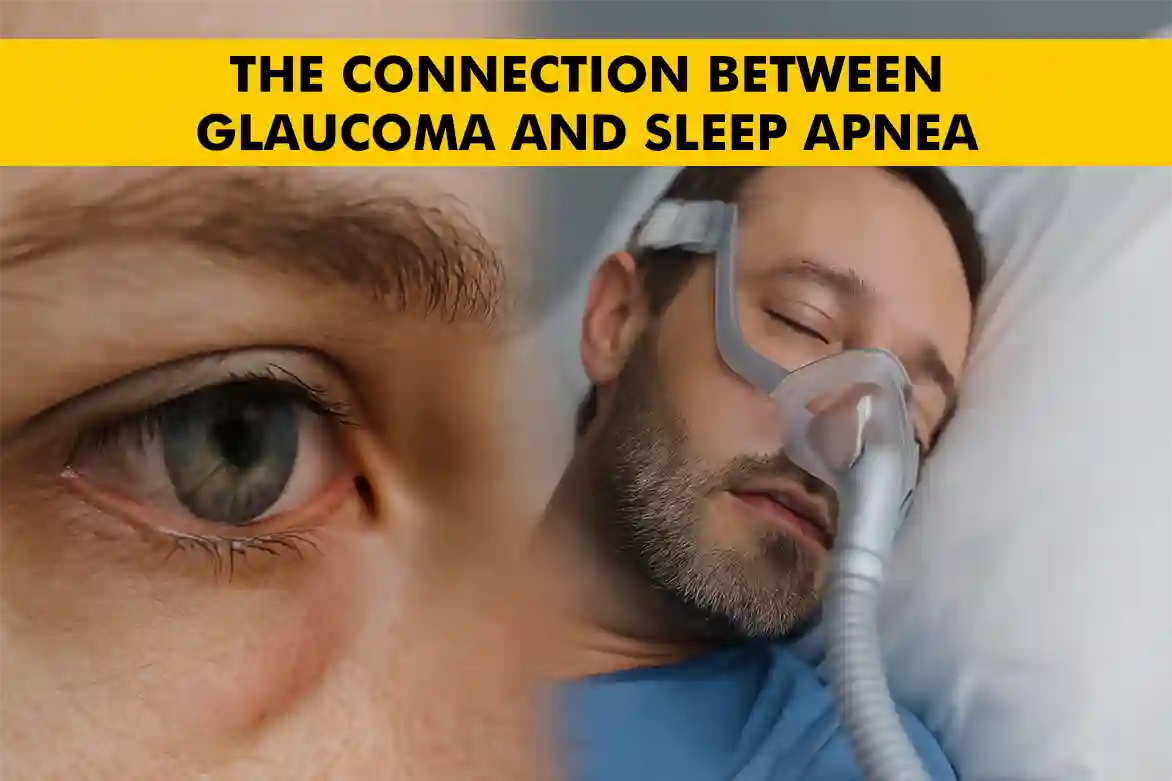
Sleep and vision might seem like unrelated aspects of health, but emerging research indicates a surprising link between them. Specifically, studies suggest a connection between sleep apnea, one of the common sleep disorders, and glaucoma, a leading cause of blindness. This blog aims to explore how these two conditions are interrelated and what you can do to protect your health.
Understanding Glaucoma: The Silent Thief of Sight
Glaucoma is often referred to as the ‘silent thief of sight’ because it typically progresses without any early symptoms, quietly stealing vision over time. Characterized by optic nerve damage, it can lead to irreversible vision loss if left untreated, making early detection crucial. The most common form is open-angle glaucoma, which develops slowly over time, often going unnoticed until significant damage has occurred. Another form, angle-closure glaucoma, can appear suddenly and is considered a medical emergency due to its rapid onset and potential for severe vision impairment. It’s important to note that while anyone can develop glaucoma, certain factors such as age, family history, and certain medical conditions can increase the risk. Regular eye exams are essential for early detection and management, potentially preserving vision and improving quality of life.
What Is Sleep Apnea and How Does It Affect Your Health?
Sleep apnea is one of the prevalent sleep disorders that significantly impacts the quality of rest and overall health. It is characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep, which can occur dozens or even hundreds of times throughout the night. These interruptions are often brief but can severely disrupt the sleep cycle, leading to poor sleep quality and various health issues.
The most common form of this disorder is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). This type occurs when the muscles in the throat relax excessively, causing a blockage of the airway. As a result, individuals with OSA may experience loud snoring, which is often the first noticeable symptom.
If left untreated, sleep apnea can lead to a range of severe health complications. The repeated drops in oxygen levels during sleep can strain the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of developing conditions such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and even stroke.
Unveiling the Link: How Sleep Apnea Can Lead to Glaucoma
Recent research suggests a link between sleep apnea and glaucoma. Sleep apnea involves repeated breathing interruptions during sleep, causing oxygen level drops. These drops can increase intraocular pressure, a risk factor for glaucoma, potentially damaging the optic nerve and leading to gradual vision loss without early symptoms.
Sleep apnea also causes systemic inflammation and oxidative stress, harming tissues, including the eyes. Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress can increase the risk of optic nerve damage, making those with sleep apnea more prone to glaucoma.
Understanding this link is vital for managing sleep apnea to improve sleep and protect eye health. Treatments like CPAP therapy can help maintain oxygen levels, reducing glaucoma risk. This highlights the importance of a holistic health approach, where treating one condition benefits another, preserving vision and well-being.
Symptoms to Watch For: Could You Be at Risk?
Common indicators of glaucoma include:
- Blurred vision: This refers to unclear or fuzzy sight.
- Halos around lights: This means seeing bright circles or rings around light sources.
- Gradual loss of peripheral vision: This involves a slow reduction in the ability to see objects outside the direct line of sight.
For sleep apnea, be aware of:
- Loud snoring: This is characterized by noisy breathing during sleep.
- Waking up with a dry mouth: This means having a parched or dehydrated feeling in the mouth upon waking.
- Feeling excessively tired during the day: This refers to experiencing extreme fatigue or drowsiness while awake.
If you notice any of these signs, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Both Conditions
Diagnosing glaucoma requires a comprehensive eye examination conducted by an eye care professional. This examination includes measuring intraocular pressure using a tonometer, inspecting the optic nerve for any signs of damage through ophthalmoscopy, and conducting visual field tests to assess peripheral vision. Additional tests, such as pachymetry to measure corneal thickness and gonioscopy to examine the drainage angle of the eye, may also be performed to provide a complete assessment.
For diagnosing sleep apnea, a sleep study, known as polysomnography, is typically conducted. This study can be performed in a sleep laboratory, where various physiological parameters such as brain activity, eye movements, heart rate, and breathing patterns are monitored overnight. Alternatively, a home sleep apnea test may be used, which involves wearing a portable device that records similar data while the patient sleeps in their own bed.
Treatment for glaucoma often begins with prescription eye drops designed to lower intraocular pressure, thereby preventing further optic nerve damage. If medications are insufficient, laser therapy, such as trabeculoplasty, may be employed to improve fluid drainage from the eye. In more advanced cases, surgical procedures like trabeculectomy or the insertion of drainage implants may be necessary to control the condition.
In contrast, the primary treatment for sleep apnea is the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy. This involves wearing a mask over the nose or mouth during sleep, which delivers a steady stream of air to keep the airways open. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as weight loss, avoiding alcohol and sedatives, and sleeping on one’s side can significantly improve symptoms. In some cases, oral appliances or surgery may be recommended to address anatomical issues contributing to the disorder.
Prevention and Management
Prevention of Glaucoma:
- Schedule regular eye examinations, especially if you have risk factors like family history, advancing age, or medical issues such as diabetes.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle by managing blood pressure.
- Avoid smoking to further reduce the risk.
Management of Sleep Apnea:
- Achieve and maintain a healthy weight to prevent airway obstruction.
- Avoid alcohol and smoking to reduce symptom exacerbation.
- Use CPAP therapy consistently to keep airways open and improve oxygen levels.
- Consider positional therapy, such as sleeping on your side, for additional benefits.
By following these preventive and management strategies, you can significantly reduce the risk of severe health complications related to glaucoma and sleep apnea.
Conclusion
The link between glaucoma and sleep apnea underscores the importance of a holistic approach to health. Regular check-ups, early diagnosis, and effective treatment can make a significant difference. By understanding the connection between these two conditions, you can take steps to protect both your vision and your overall well-being.
FAQs
Yes, untreated sleep apnea can lead to permanent eye damage, including glaucoma.
CPAP therapy has been shown to reduce the risk of developing glaucoma by improving oxygen levels and reducing intraocular pressure.
Early warning signs of glaucoma include subtle changes in vision and eye discomfort, so regular eye exams are crucial.
Sleep apnea patients should get eye exams at least once a year.
Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and managing blood pressure can help prevent both conditions.